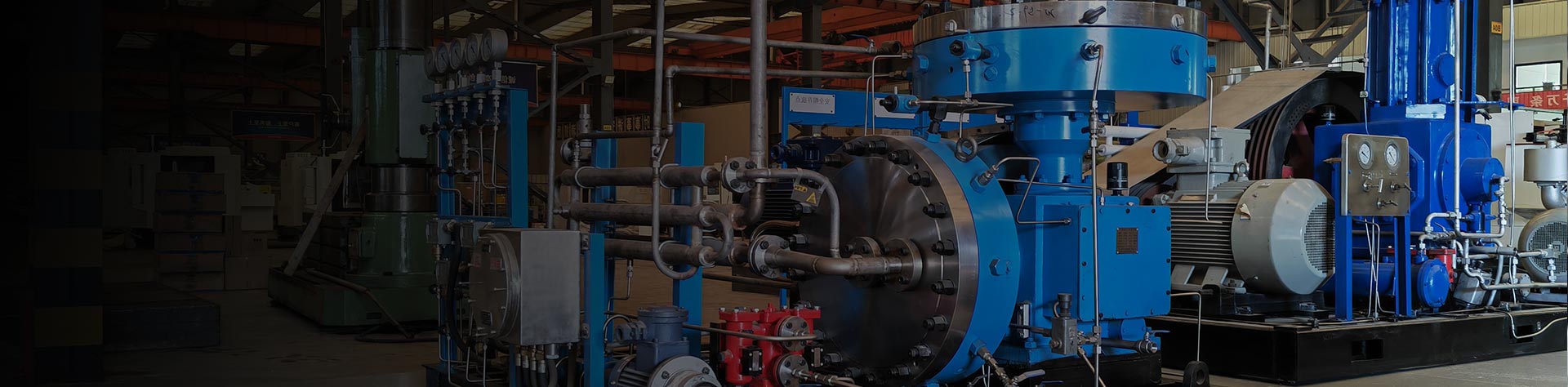
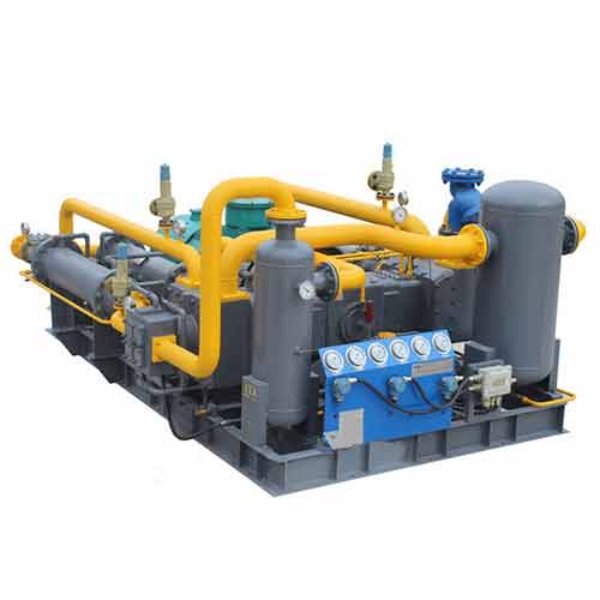
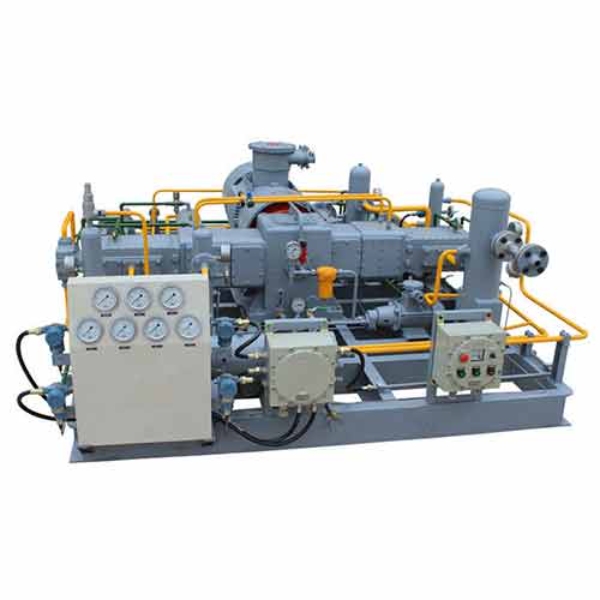
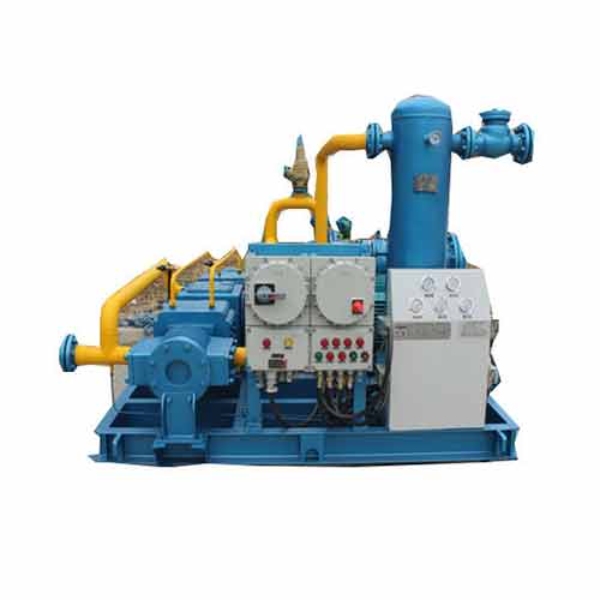
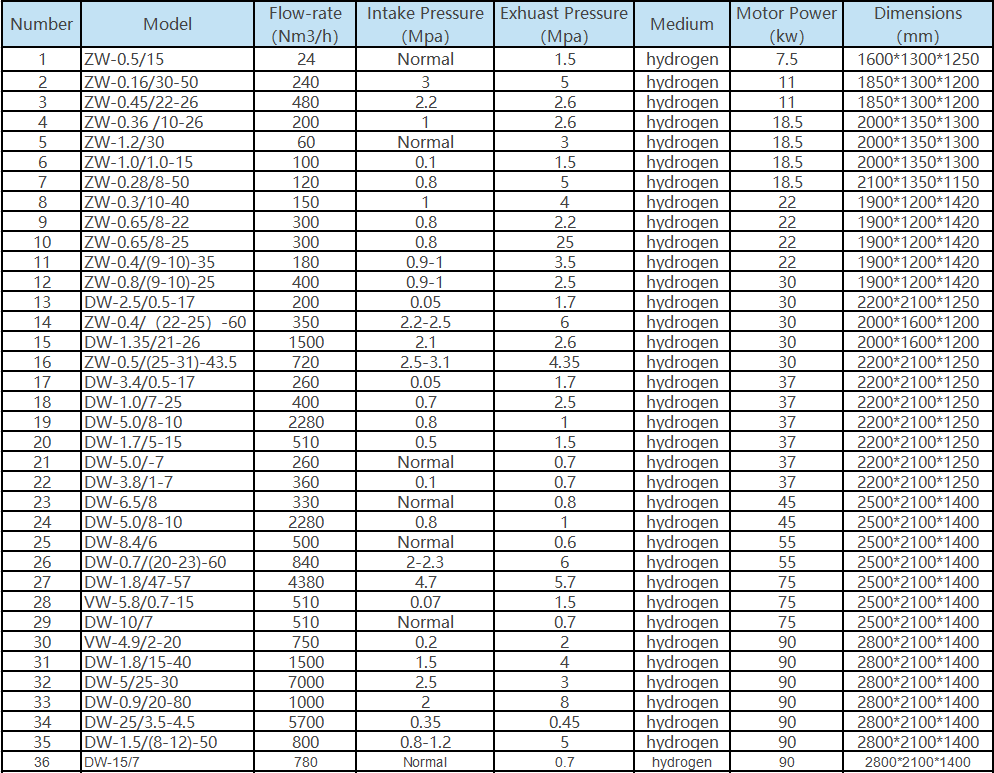
Hydrogen Industry Compressor
Hydrogen Industry Compressor
- Brand Huayan Gas
- Place of Origin China·Xuzhou
- Compressor structure Piston Compressor
- Volume flow 3NM3/hour~1000NM3/hour (customized)
- Voltage: 380V/50Hz (customized)
- Maximum outlet pressure 100MPa (customized)
- Crankshaft speed 350~420 rpm/min
- Certificate ISO9001, CE certificate, etc.
Get Free Quote
Description
A hydrogen Industry compressor is a specialized device designed to increase hydrogen gas pressure. Hydrogen, a lightweight and highly flammable gas, is often used in various industrial applications, including fuel cells, chemical processing, and transportation. The hydrogen compressor works by drawing in hydrogen gas at a lower pressure and then compressing it to a higher pressure. This increase in pressure is crucial for storing and transporting hydrogen efficiently and facilitating certain chemical reactions and industrial processes.
Features & Characteristics:
- Maintenance Monitoring and Predictive Maintenance: Some hydrogen compressors come equipped with sensors and monitoring systems that track the condition of key components. This data is then used to implement predictive maintenance strategies, helping to anticipate and address potential issues before they lead to downtime.
- Hydrogen Recirculation Systems: In certain applications, hydrogen compressors may incorporate recirculation systems to optimize gas flow and reduce energy consumption. These systems enhance overall efficiency by recirculating part of the compressed hydrogen back into the compression process.
- Corrosion Resistance: Hydrogen compressor components are often constructed from materials that resist corrosion, ensuring the longevity of the equipment even when exposed to hydrogen gas, which can be corrosive under certain conditions.
- Fail-Safe Mechanisms: Fail-safe mechanisms are crucial for preventing catastrophic failures. Hydrogen compressors include safety features and fail-safe mechanisms to automatically shut down or take corrective actions in abnormal operating conditions.
- Hydrogen Quality Certification: Compressors may undergo hydrogen quality certification for applications where hydrogen purity is critical to validate that the compressed gas meets specific purity standards. This certification assures industries such as electronics manufacturing and fuel cell development.
Main Structure: Hydrogen Industry Compressor
- Compression Chamber: Central space for compressing hydrogen gas.
- Piston (in Piston Compressors): Moves within a cylinder to reduce chamber volume.
- Diaphragm (in Diaphragm Compressors): Flexible diaphragms compress gas in a sealed chamber.
- Impeller (in Centrifugal Compressors): A rotating element imparts kinetic energy to the gas.
- Drive Mechanism: Powers compressing elements (electric motor, engine, etc.).
- Valves: Control gas flow in and out of the compression chamber.
- Cooling System: Prevents overheating by dissipating generated heat.
- Safety Features: Includes relief valves, sensors, and emergency shutdown systems.
- Control System: Manages valve timing, pressure, and overall system stability.
- Materials Selection: Uses alloys and coatings resistant to hydrogen embrittlement.
- Instrumentation: Monitors parameters like pressure, temperature, and vibration.
- Frame and Housing: Provides structural support, protection, and may reduce noise.
Applications: Hydrogen Industry Compressor
- Power Generation: Hydrogen can be used in gas turbines or internal combustion engines for power generation. Compressed hydrogen is essential for these applications, and hydrogen compressors supply high-pressure hydrogen to power generation facilities.
- Grid Balancing: Compressed hydrogen can be used for grid balancing, storing excess energy generated from intermittent renewable sources. Hydrogen compressors enable hydrogen compression for storage and subsequent use in fuel cells.
- Hydrogen Blending in Natural Gas Networks: Compressed hydrogen can be blended with natural gas in existing pipelines to reduce the carbon intensity of the gas supply. Hydrogen compressors are used to pressurize hydrogen for injection into natural gas grids.
- Hydrogen-Powered Marine Transportation: Hydrogen fuel cells are being explored for use in maritime transport. Hydrogen compressors play a role in providing high-pressure hydrogen for fuel cells in ships and vessels.
- Hydrogen Storage in Metal Hydrides: Hydrogen can be stored in metal hydrides, and compressors are used to pressurize hydrogen for absorption into these materials, providing an alternative means of hydrogen storage.