Hydrogen Sulfide Compressor: Efficient Solutions for Gas Processing Plants
Hydrogen sulfide compressor is an extremely hazardous and flammable gas that is commonly found in industrial operations such as oil and gas extraction, wastewater treatment, and chemical synthesis. Hydrogen sulfide compressors are tools designed to raise their pressure to allow safe transportation via pipelines or storage tanks.

Hydrogen sulfide compression requires using compressors specifically designed to handle its harsh gas conditions. Compressor design and materials play a pivotal role in its efficiency, safety, and environmental impact – an especially essential factor considering hydrogen sulfide’s highly toxic and explosive nature. Finally, regular operation and maintenance must take place to ensure optimal performance from your compressor over its lifespan.
Key Takeaways
- Hydrogen sulfide compressors are tools used to increase the pressure of hydrogen gas for safe transport through pipelines or storage tanks.
- The design and materials of compressors are crucial elements that impact their efficiency, safety, and environmental footprint.
- Proper operation and maintenance are crucial to ensure the long-term efficiency and optimal performance of a compressor.
Fundamentals of Hydrogen Sulfide Compression
Compression Principles
Hydrogen Sulfide compressors are devices used to compress gas streams that contain H2S. Compressing this gas increases its pressure, making it easier to transport and process. Compression works by decreasing volume; increasing pressure; or shrinking space containing it all together.
There are different kinds of compressors used for hydrogen sulfide compression, including reciprocating, rotary, and centrifugal models. Each has its own set of advantages and disadvantages depending on the application – for instance, reciprocating compressors are best suited for low flow rates with high pressure ratios while centrifugal ones excel with both characteristics in mind.
Hydrogen Sulfide Characteristics
Hydrogen sulfide is a colorless gas with an intense sulfur smell. Highly toxic and potentially lethal at higher concentrations, even 20 ppm in air can be dangerous to human health; at 800 ppm it can kill within 30 minutes due to destruction of lung tissues.
Compressing gas streams containing H2S requires careful consideration of its specific characteristics. H2S can be highly corrosive, which could damage equipment including compressors. Furthermore, its low boiling point means it could condense at lower temperatures and cause blockages within the compressor itself. To counteract these potential issues, special materials and coatings are applied to compressor components while heating can prevent condensation of H2S gas streams.
Hydrogen sulfide compression is an integral process in the oil and gas industry. It ensures safe transport and processing of H2S gas streams. By understanding its characteristics, operators can select an ideal compressor to ensure this process runs efficiently and safely.
Design and Materials Considerations of Compressor
Material Selection
When designing a hydrogen sulfide compressor, material selection is of utmost importance. Compressor components in contact with H2S gas must adhere to NACE MR-1075 in order to avoid stress cracking of H2S molecules.
Ariel Corporation suggests using 17-4PH stainless steel piston rod material in double H1150 condition per NACE MR-0175 and with maximum Rc 33 chromium content when compressing gas that contains H2S.
Ro-Flo compressors are specifically engineered for use in extreme gas environments, including those containing hydrogen sulfide. Their heads and cylinders feature materials that comply with NACE MR-1075 to help minimize stress cracking during operation.
Corrosion Considerations
Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) can be toxic and lethal. When compressing gas containing H2S, it is vital to take note of any corrosion risks that might occur.
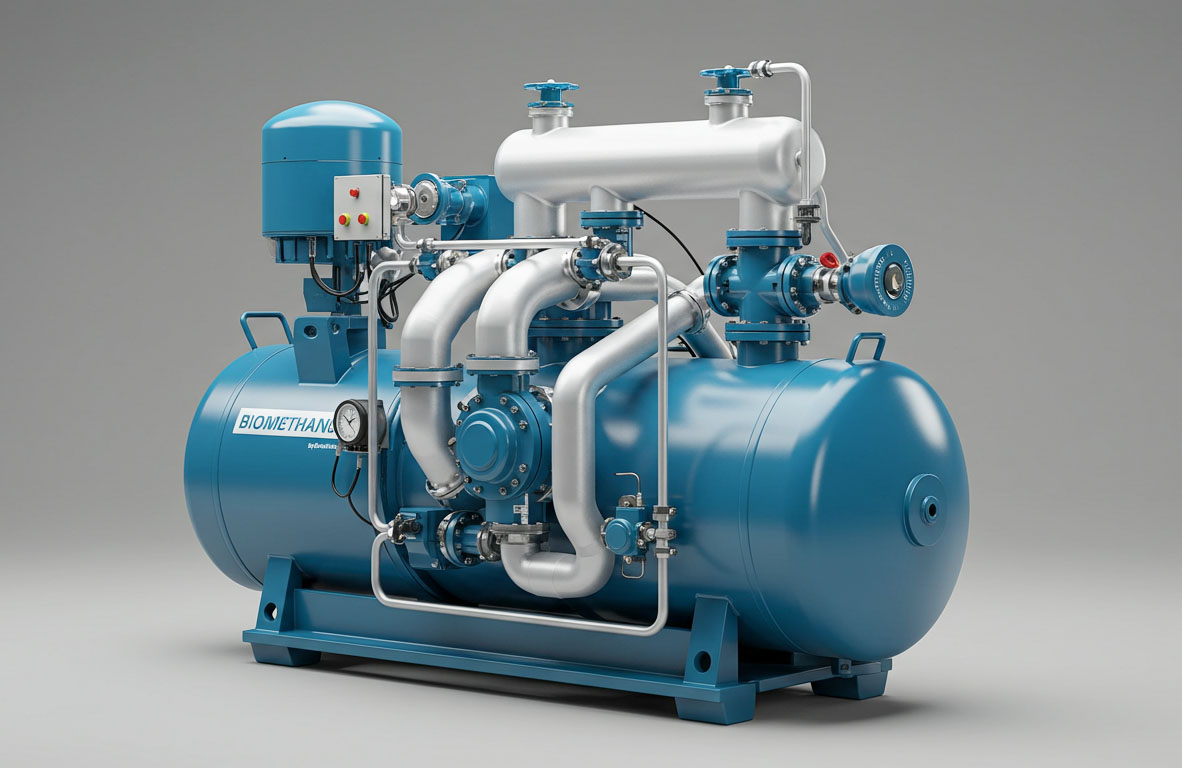
Huayan’s hydrogen sulfide compressor is specifically designed to compress and transport hydrogen sulfide gas efficiently, improving flow rate while optimizing production processes. Controlling pressure of hydrogen sulfide gas is vital in order to preserve ideal conditions in chemical reactions or industrial processes that use hydrogen sulfide.
To prevent corrosion caused by H2S gas, it is crucial to select materials which are resistant. Ariel Corporation recommends the use of 17-4PH stainless steel piston rod material with maximum Rc 33 chromium content when compressing gas containing H2S. Ro-Flo compressors have also been constructed with materials which meet NACE MR-1075 requirements, making them suitable options for compressing this kind of gas.
As previously discussed, when designing a hydrogen sulfide compressor it is essential that materials that comply with NACE MR-1075 are chosen, and are resistant to H2S gas. Regulating pressure of H2S gas is key in maintaining optimal conditions during chemical reactions or industrial processes using it.
Safety and Environmental Considerations
Hazardous Gas Handling
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is a hazardous gas that can cause serious health effects, including respiratory failure, unconsciousness, and death. Therefore, it is important to handle this gas with extreme care. The use of personal protective equipment (PPE), such as respirators, gloves, and eye protection, is essential when handling H2S. The PPE should be selected based on the level of exposure and the type of work being performed.
In addition to PPE, proper ventilation is necessary to prevent the buildup of H2S gas. The use of gas detectors and alarms is also recommended to alert workers of the presence of H2S gas in the environment. It is important to follow all safety guidelines and procedures when handling H2S to prevent accidents and injuries.
Emission Controls
The management of H2S emissions is of utmost importance in industries such as oil and gas, wastewater treatment, and various sectors dealing with environmental and energy concerns. The use of hydrogen sulfide compressors, such as the Huayan’s Hydrogen Sulfide Compressor, can help control and reduce H2S emissions.
In addition to the use of compressors, other emission control techniques include the use of scrubbers, filters, and flares. Scrubbers remove H2S from gas streams by contacting the gas with a liquid, while filters remove H2S from gas streams by passing the gas through a medium that absorbs the H2S. Flares are used to burn off H2S gas, converting it into less harmful compounds.
It is important to use the appropriate emission control techniques based on the specific industry and application to prevent harm to the environment and human health.
Operation and Maintenance

Routine Maintenance
Like any other type of compressor, hydrogen sulfide compressors require routine maintenance to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Routine maintenance tasks for a hydrogen sulfide compressor include checking the oil levels, inspecting the belts and hoses, and cleaning the compressor’s air filters. It is important to adhere to the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule to prevent costly breakdowns and extend the life of the compressor.
Operational Best Practices
In addition to routine maintenance, there are several best practices that operators should follow when operating a hydrogen sulfide compressor. These practices include:
- Monitoring the compressor’s temperature and pressure levels regularly to ensure they remain within safe operating limits.
- Using only approved lubricants and coolants to prevent damage to the compressor’s internal components.
- Ensuring that all safety equipment, such as gas detectors and emergency shutdown systems, are in good working order and are regularly tested.
- Following all applicable safety regulations and guidelines to prevent exposure to hydrogen sulfide gas, which is highly toxic and can be lethal in high concentrations.
By following these best practices and adhering to the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule, operators can ensure that their hydrogen sulfide compressor operates safely and efficiently for many years to come.
Industry Applications

Hydrogen sulfide compressors find their applications in various industries that deal with environmental and energy concerns. Some of the industries that use hydrogen sulfide compressors are:
Oil and Gas Industry
The oil and gas industries are major users of hydrogen sulfide compressors. Hydrogen sulfide emissions pose serious health risks to workers in this industry; hence it’s critical that they are managed effectively using hydrogen sulfide compressors for safe transporting of the gas stream containing hydrogen sulfide.
Waste Water Treatment
Waste Water treatment plants utilize hydrogen sulfide compressors as part of their anaerobic digestion processes, where hydrogen sulfide gas is often a byproduct. Since hydrogen sulfide gas can be harmful and smell unpleasant, it must be removed before being released back into the environment – for which hydrogen sulfide compressors provide effective solutions. Hydrogen sulfide compressors compress gas streams that contain hydrogen sulfide to help remove it efficiently from this gas stream and eliminate its presence before being released back into the atmosphere – thus helping remove all hydrogen sulfide gasses from being released back into the atmosphere.
Hydrogen sulfide compressors can also aid in producing clean hydrogen energy by purifying hydrogen sulfide. This involves breaking it down into hydrogen and sulfur for use as source materials in making energy from hydrogen sulfide; hydrogen sulfide compressors ensure safe and efficient transportation of this process.
Hydrogen sulfide compressors find applications across many industries that deal with environmental and energy concerns, including oil & gas and wastewater treatment industries. The primary industries using hydrogen sulfide compressors include these two sectors.