CH4 Compressor: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Features and Benefits
CH4 Compressor Natural Gas (CNG) offers an alternative fuel option to traditional vehicular fuels. Composed primarily of methane (CH4) compressed to less than one percent of its volume at standard atmospheric pressure, CNG offers several advantages over its more traditional alternatives such as lower greenhouse gas emissions, reduced costs and enhanced engine performance.

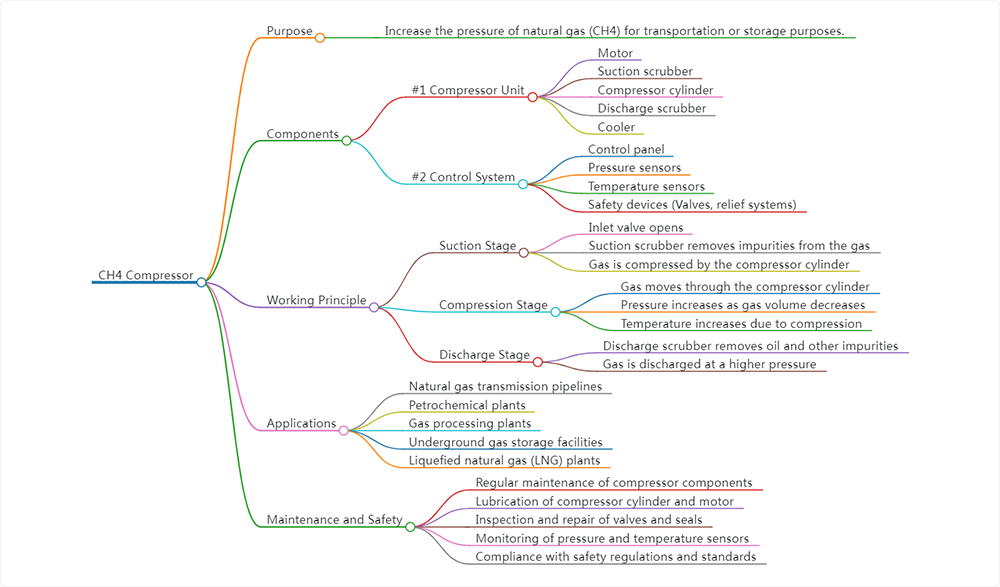
CH4 compressors are integral components of any CNG fueling station, as they compress natural gas to its required pressure and store it in high-pressure cylinders. Their design takes into account natural gas’s unique properties such as its low lubricity and high moisture content, among others. There are various types of compressors available – reciprocating, rotary screw and centrifugal are some examples that exist – with each offering advantages and disadvantages depending on which is chosen based on specific applications.
Key Takeaways
- CH4 compressors are an essential component of CNG fueling stations.
- There are several types of compressors available, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
- The choice of compressor depends on the specific application.
Fundamentals of CH4 Compressor Fundamentals
Types of CH4 Compressors
There are various types of compressors used to compress CH4 gas. The most widely-used models include reciprocating and centrifugal compressors. Reciprocating compressors use positive displacement pistons while centrifugal compressors employ rotating impellers to compress it.
Principles of Operation
Reciprocating compressors work by drawing in gas on the intake stroke and compressing it on the compression stroke before discharging it out through their discharge port. Reciprocating compressors are typically used for low flow rates with high-pressure applications.
Centrifugal compressors use a rotating impeller to accelerate gas to high velocities before passing it through a diffuser to be converted to pressure energy by pressure differential. Centrifugal compressors are typically utilized for high flow rates with lower pressure requirements.
Both types of compressors can be used to compress CH4 gas. Your choice will depend on your application needs; reciprocating compressors tend to be more efficient at low flow rates while centrifugal ones offer greater performance at high flow rates.
CH4 compressors are used to compress CH4 gas and are available in multiple varieties – reciprocating compressors and centrifugal compressors are two common types. Your choice will ultimately depend upon your application requirements.
Design and Specifications
Materials and Components
Materials and Components The CH4 compressor is a centrifugal compressor designed to compress natural gas. The CH4 is composed of several components including its casing, impeller, diffuser and bearings – each made of high-grade materials to ensure durability during natural gas compression.
The compressor casings typically consist of cast iron or steel while their impeller is typically composed of aluminum or steel. A diffuser made from stainless steel is often employed while bearings are composed of high strength materials like ceramic or tungsten carbide to increase efficiency and ensure reliable performance.
Performance Parameters
The CH4 compressor was designed to operate within specific performance parameters. These include mass flow rate, pressure ratio, and efficiency. Mass flow rate measures how much gas the compressor can handle per unit time (typically measured in cubic meters per second or cubic feet per minute); pressure ratio refers to the ratio between discharge pressure and suction pressure produced by the compressor; efficiency refers to how effectively actual work done compares with theoretical work possible by it;
CH4 compressor performance can be affected by several factors, including its design components, operating conditions and gas properties. Compressors are usually intended to run at specific speeds which are determined by both impeller diameter and gas properties such as density/viscosity levels in the gas being compressed. Impeller diameter should meet mass flow rate requirements while gas density/viscosity levels help shape component sizes/shape.
Overall, the CH4 compressor is an extremely high-quality centrifugal compressor designed to compress natural gas. All materials and components used in its construction were carefully chosen to ensure durability under harsh natural gas compression conditions. Performance depends on many factors including its design components, operating conditions and gas properties.
Installation and Commissioning
Installing and commissioning a CH4 compressor requires meticulous planning and execution in order to ensure its optimal operation and safety. Here are the steps needed for installing and commissioning one:
1. Site Preparation
Before installing the compressor, its site should be prepared by making sure that it is clean, dry and level. Any obstacles that could affect its functioning should also be cleared away; ventilation should also be considered along with sufficient lighting in this process.
2. Installation
It is essential that a CH4 compressor be installed according to its manufacturer’s instructions, with its base secured using bolts for optimal results. Pipework and wiring must also adhere to local codes and regulations.
3. Electrical Connections
All electrical connections should be completed by a trained electrician. To comply with local codes and regulations, connect the compressor to an appropriate-sized circuit that has been properly grounded; all connections should then be thoroughly examined to ensure tightness and proper insulation.
4. Commissioning
Incorporating the CH4 compressor involves conducting tests and adjustments on its performance to ensure its optimal operation and safety. For proper commissioning of this appliance, these steps must be followed:
- Check the oil level and add oil as necessary.
- Check the air filter and replace it if necessary.
- Check the belt tension and adjust it if necessary.
- Check the pressure relief valve and ensure that it is functioning properly.
- Start the compressor and monitor its performance.
- Adjust the pressure switch to the desired operating pressure.
- Check for leaks in the piping and fittings.
- Record all operating parameters and compare them to the manufacturer’s specifications.
By following these steps, the CH4 compressor can be installed and commissioned safely and efficiently. It is important to note that regular maintenance and inspections should be performed to ensure that the compressor continues to operate safely and efficiently.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting

Routine Maintenance Procedures
Routine maintenance is essential to keep CH4 compressors running at optimal performance and to prevent downtime due to unexpected failures. The following are some recommended maintenance procedures:
- Regularly check the oil level and top it up if necessary. Ensure that the oil is clean and free of contaminants.
- Check the air filters and clean or replace them as necessary. Dirty filters can reduce the efficiency of the compressor and cause it to work harder than it needs to.
- Inspect the belts and pulleys for wear and replace them if necessary.
- Check the safety valves and pressure switches to ensure they are functioning correctly.
- Inspect the compressor’s electrical connections and tighten them if necessary.
- Check the cooling system and clean the radiator if it is dirty.
Following these routine maintenance procedures can help prevent common issues and ensure the longevity of the compressor.
Common Issues and Solutions
Despite regular maintenance, CH4 compressors can still experience issues. Below are some common issues and their solutions:
- Compressor not starting: Check the power source and ensure that the compressor is plugged in and switched on. Check the fuses and circuit breakers. If the problem persists, contact a qualified technician.
- Compressor running but not producing air: Check the air filters and clean or replace them if necessary. Check the pressure switch and ensure that it is set correctly. Check the intake valve and ensure that it is not blocked.
- Compressor producing excessive noise: Check the belts and pulleys for wear and replace them if necessary. Check the oil level and ensure that it is at the correct level. Check the motor bearings and replace them if necessary.
- Compressor overheating: Check the cooling system and ensure that the radiator is clean and free of debris. Check the oil level and ensure that it is at the correct level. Check the belts and pulleys for wear and replace them if necessary.
In summary, routine maintenance is essential for the longevity and optimal performance of CH4 compressors. By following recommended maintenance procedures and addressing common issues promptly, users can minimize downtime and maximize productivity.
Regulations and Safety

Industry Standards
When it comes to the CH4 compressor, there are a number of industry standards that must be followed to ensure safe and efficient operation. The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) provides a number of standards for pressure vessels, which includes compressors. These standards ensure that the compressor is designed and manufactured to meet certain safety requirements.
Another important standard is the Compressed Gas Association (CGA) standard, which provides guidelines for the handling, storage, and use of compressed gases. This standard is important for the CH4 compressor as it deals with the handling of the gas that is being compressed.
Safety Protocols
In addition to following industry standards, there are a number of safety protocols that must be followed when operating the CH4 compressor. One important safety protocol is to ensure that the compressor is properly grounded. This is important to prevent any electrical shock or damage to the equipment.
Another important safety protocol is to ensure that the compressor is properly ventilated. This is important to prevent the buildup of any potentially harmful gases that may be present during the compression process.
It is also important to ensure that the compressor is properly maintained and inspected on a regular basis. This includes checking the oil levels, filters, and other components to ensure that they are functioning properly.
By following these industry standards and safety protocols, the CH4 compressor can be operated safely and efficiently.
Frequently Asked Questions

What factors influence the pricing of CH4 compressors?
The pricing of CH4 compressors is influenced by several factors such as the compressor’s capacity, power rating, and design. Other factors that affect the pricing include the manufacturer’s reputation, quality of materials used, and after-sales support. The capacity of the compressor is determined by the amount of gas it can compress per unit time. The power rating refers to the amount of energy required to operate the compressor. Generally, compressors with higher capacity and power rating cost more.
Which components are critical for the maintenance of CH4 compressors?
Several components are critical for the maintenance of CH4 compressors. These include the compressor’s valves, pistons, and cylinders. The valves control the flow of gas into and out of the compressor, while the pistons compress the gas. The cylinders are the chambers where the pistons move up and down to compress the gas. The compressor’s oil and filters are also critical for maintenance. The oil lubricates the moving parts, while the filters remove contaminants from the gas and oil.
How do CH4 compressors differ among manufacturers?
CH4 compressors differ among manufacturers in terms of design, capacity, and performance. Some manufacturers specialize in producing compressors for specific applications, such as biogas or natural gas compression. Others produce compressors with different features, such as variable speed drives, which allow the compressor to adjust its speed based on the gas demand. The quality of materials used and after-sales support also differ among manufacturers.
What are the typical applications of biogas compressors in industry?
Biogas compressors are used in several applications in the industry, such as wastewater treatment plants, landfills, and agricultural facilities. These compressors are used to compress biogas produced from organic waste, such as food waste, animal manure, and sewage sludge. The compressed biogas can then be used as fuel for generators, boilers, or vehicles.
What is the process for compressing methane for effective storage?
The process for compressing methane for effective storage involves several steps. First, the methane is extracted from its source, such as a natural gas well or biogas digester. The gas is then purified to remove impurities such as water and carbon dioxide. The purified gas is then compressed using a CH4 compressor to increase its density and reduce its volume. The compressed gas is stored in tanks or pipelines for later use.
Why is methane less commonly used as a fuel in automotive engines?
Methane is less often used as an automotive engine fuel due to a variety of reasons, primarily related to lack of infrastructure for refueling methane-powered vehicles and its lower energy density compared to gasoline or diesel; furthermore, methane’s lower octane rating reduces engine performance; yet in countries like China and India it is frequently employed as bus and truck fuels.


